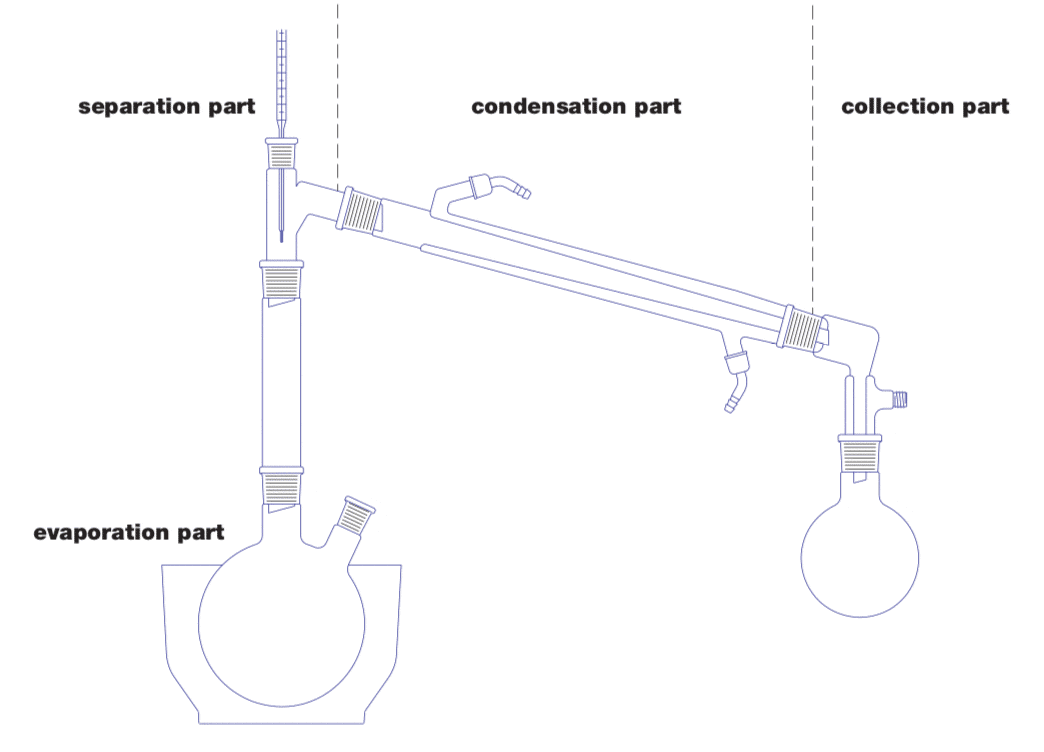
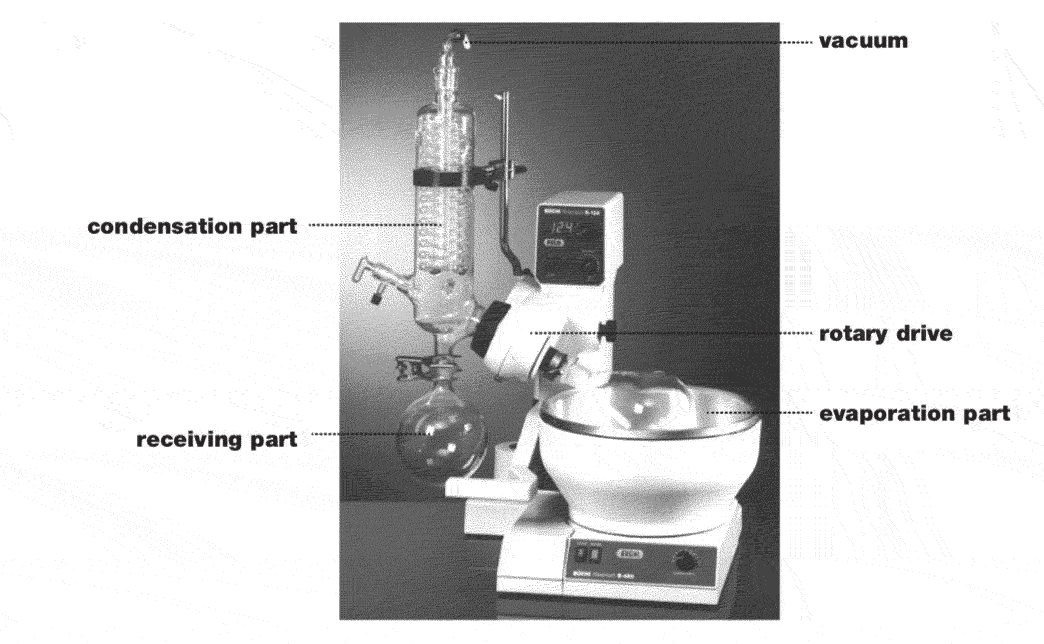
Basic construction of distillation apparatus
| Evaporation part | This is where the mixture is made to evaporate by heating. |
| Separation/ fractional part | This is where the actual separation of solvent and non-volatile or less volatile components takes place. |
| Condensation/ cooling part | Originally this section was only required when the distillate was to be reused. Today, condensation should be as complete as possible for environmental reasons. |
| Collection part | This is where the various condensates are collected. |
What is a rotary evaporator?
A rotary evaporator is a specially designed instrument for the evaporation of solvent (single-stage or straight distillation) under vacuum. The evaporator consists of a heating bath with a rotating flask, in which the liquid is distributed as a thin film over the hot wall surfaces and can evaporate easily. The evaporation rate is regulated by the heating bath temperature, the size of flask, the pressure of distillation and the speed of rotation.
Functional principle of a rotary evaporator
| Evaporation part | The solvent is heated via the heating bath. A thin film of solvent forms on the inner surface of the rotating evaporating flask, resulting in a higher rate of evaporation. Rotation ensures homogenous mixing of the sample and prevents overheating inside the flask. |
| Rotary drive | The drive unit provides constant rotation of the evaporating flask for the reasons stated above. |
| Condensation part | The solvent vapor flows at high speed into the condensation part (con- denser) of the rotary evaporator. At this point the energy inside the sol- vent vapor is transferred to the cooling medium (usually water) and the solvent condenses. The condensed solvent now flows by force of gravity into the receiving flask. |
| Receiving flask | The receiving flask is used to collect the condensed solvent. |
| Vacuum | Vacuum is used to lower the boiling temperature and hence raise the efficiency of the distillation process. |
Advantages of the rotary evaporator
(Compared with static apparatus)
With a vacuum rotary evaporator you can carry out single-stage distillation runs quickly and gently.
The evaporation capacity of a rotary evaporator is about 4 times greater than that of a conventional, static distillation apparatus. Heat transmission in the heating bath as well as inside the flask is greatly improved by rotation of the evaporating flask. Rotation greatly enlarges the active surface inside the flask, hastening the evaporation. With the liquid remaining at any one point of the flask wall for a short time only, it is subject to minimum stress during the distillation (no overheating, no incrustation). Bumping and foaming are greatly reduced by the rotation.
Rotary evaporators are used for
- Distillation of solvent
- Concentration of solutions and suspensions Crystallization or recrystallization
- Synthesis and purifying of fine chemicals Soxhlet extraction
- Powder and granules drying
- Recycling of solvent